
A Comprehensive Guide to Customer Data Platform
Table of Contents
Recollect the last time you purchased a laptop. You did extensive research, and when you ultimately decided what type of laptop to purchase, you probably researched the finest place for purchasing. You must have visited some additional websites to compare costs, return policies, shipping items, and more. You may have interacted several times with the company you finally purchased from via email, Facebook ads, live chat, or website visits.
You must have noticed that with every interaction, your experience with the company felt much more personalized to you. Their email follow-up, the relevance of their Facebook ads, and the subtle changes made by the websites to seem more personal according to your search despite being automated felt as if it was perfectly crafted for you. The companies do this using CDP (Consumer Data Platform), to personalize their marketing to you.
Customer Data Platform
A CDP is software that aggregates as well as organizes customer data over various touchpoints; also used by some other marketing efforts, systems, and software. CDPs collect as well as structure data in real-time into centralized, individual customer profiles. It is a package of software that creates a unified, persistent customer database that is accessible to the other systems. Customer profiles are built by customer data platforms by integrating data from various first, second, as well as third-party sources, including your DMP and CRM, e-commerce behavioral data, social media activity, email web forms, transactional systems, and more. The CDPs inform the people-based marketing putting the customers at the center of the flywheel.
Data that makes up CDP

To function, CDPs need functional data. CDPS exists because customer data has become quite important for both marketing and business operation. Customer data are the information that the customers leave behind when they use the internet to interact with companies offline and online through in-store interactions, e-commerce portals, blogs, and websites. It is very much valuable to businesses. However, the latest legal dialogue, like GDPR, has altered the way organizations manage and collect this data. For maximum CDPs, the customer data arrives in the form of first-party data, which means that the data that the company collects is used only for the marketing of that company. The four key types of customer data collected and organized by CDPs are-
1. Identity Data
In a CDP, the foundation of every customer profile is built by identity data. This kind of data permits the business to identify each customer uniquely as well as prevent costly replications. The identity data includes:
- Information regarding names like first and last name
- The contact information like email address and phone number
- Location information like city, address, and zip code
- Social information like LinkedIn address and Twitter handle
- Demographic information like gender and age
- Account information like company-specific account numbers and user IDs
- Professional information like company and job title
2. Descriptive Data
On the identity data, the descriptive data expands and provides the companies with a greater image of their customers. The descriptive data categories vary based on the kind of company. The data includes:
- Hobby information like gym membership and magazine subscription
- Lifestyle information like the type of home, pet, and vehicle
- Family information like marital status and the number of children
- Career information like job level, income, industry, and employers
3. Behavioral and Quantitative Data
Quantitative data permits the business to understand the pattern in which every customer is engaged in their organization through particular transactions, reactions, and actions. The quantitative data includes:
- Customer service information like service representative details, query details., and communication dates.
- Online activity information like social media engagement, product views, website click-throughs, and website visits.
- Email communication information like dates, email responses, email click-throughs, and email opens.
- Transaction information like the type and number of returned products and order dates. This also includes RMF analysis- Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value.
4. Qualitative Data
Qualitative data offers context for customer profiles and provides customer data personality. This kind of data collects any attitudes, opinions, or motivations expressed by customers of a business, irrespective of relevance to the company. This includes:
- Attitude information like favorite food, textile, animal, color
- Opinion information like how would customers rate the product, how would customers rate the customer service, or how likely would the customers recommend the company?
- Motivation information like how customers heard about the company? Or why did the customer purchase a particular product? Or what made the customers choose this particular product over the rest?
As it is noted that CDPs collect as well as organize a wide variety ofdata, it is quite important that most of the specific data, as well ascategories of data, is going to vary based on your industry and business.
CDP Use cases

The most common use cases for customer data platforms are targeted advertising and personalized customer experience. A CDP permits the companies in developing a unified customer view as well as understanding the relationships of the companies to the customers. This helps companies accomplish targeted personalization at a large scale with marketing automation, machine learning, and AI. With the help of CDP, the perfect messages reach the perfect customers at the perfect time, irrespective of whether they are available in the store or on the website. Some common use cases are mentioned below:
Marketing automation: CDP can be used to enhance the efficacy and efficiency of the marketing campaign operations of a company
Customer loyalty: Predict and measure customer loyalty, repurchase, and churn
Insights and measurements: Deep business and customer reporting
Lookalike Marketing: Advertisement across open web and social media to the audience matching the top customers
Programmatic Advertising: CDPs enable organizations to target customers in a much better way with the programmatic advertising
Predictive analytics and modeling: Determine Customer Lifetime Value, pa propensity to churn, and likelihood to buy
Customer journey orchestration: The procedure of offering a personalized experience with the customer journey, which leads to an optimal upcoming step. This process depends on strong customer data, artificial intelligence, and deep analytics to predict the best next step as a portion of the smart journey design
Customer journey optimization: Perform real-time optimizations and apply scores to customers across all channels
Retargeting: A CDS can improve retargeting precision by connecting customer data to advertising data, automating the whole process, and creating optimized audience segments.
Predictive scoring: The marketers earn the ability to predict customer behavior, such as show is likely to convert, click, purchase, or churn shortly.
Data Unification: Multiple identifiers can be associated with every customer, who stitch together an obstinate identity that is retained forever.
Personalization: Marketers can personalize the customer experience in every channel
Segmentation: CDP permits the marketers to drag and drop attributed easily and user behaviors such as social, POS, mobile, web, and other segments.
Profile Unification: The records of customer data can be combined into customers’ 360-degree view of customers permitting the companies to perform more effective personalization as well as reducing ad spend waste.
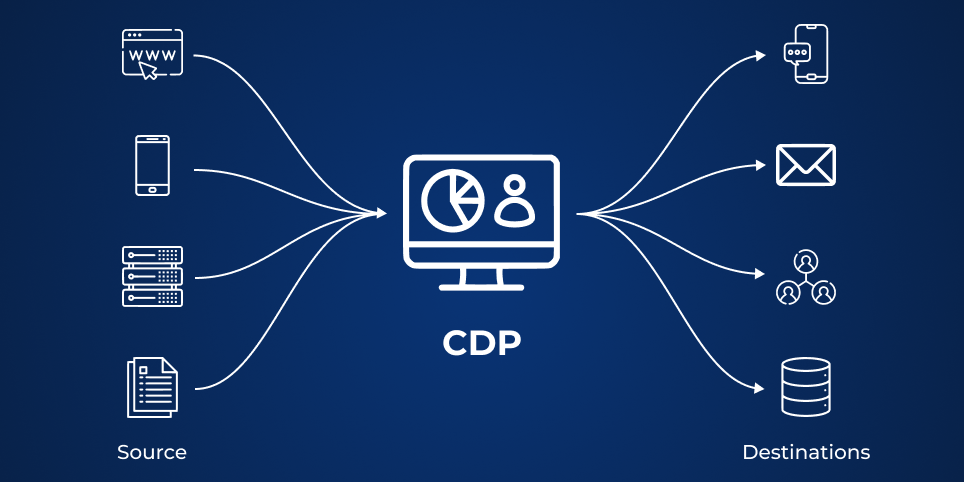

How does CDP work?
CDP in a nutshell:
Collects enrich, and cleans customer data: CDP takes care of the data collection single-handedly from all touchpoints and channels, including third and second-party resources, CRM, e-commerce, sales and marketing systems, social media, mobile, websites, and more. It then enriches and cleans data before it stores it on a centralized platform.
Draws customer insights: The users can leverage a CDP for driving customer insights based on millions of data points. These insights decode customer behavior as well as predict upcoming responses and moves based on previous patterns.
Unifies customer profiles: With the use of machine learning and AI, CDP automates customer resolution by stitching several data points, assigning a permanent ID, and attributing these to the same person. This is an integral step in customer journey orchestration and personalization.
Activates customer insights: With the use of understanding gleaned from analyzing the movements of the individualized profile, brands are now able to orchestrate the customer journey with the use of targeted actions.
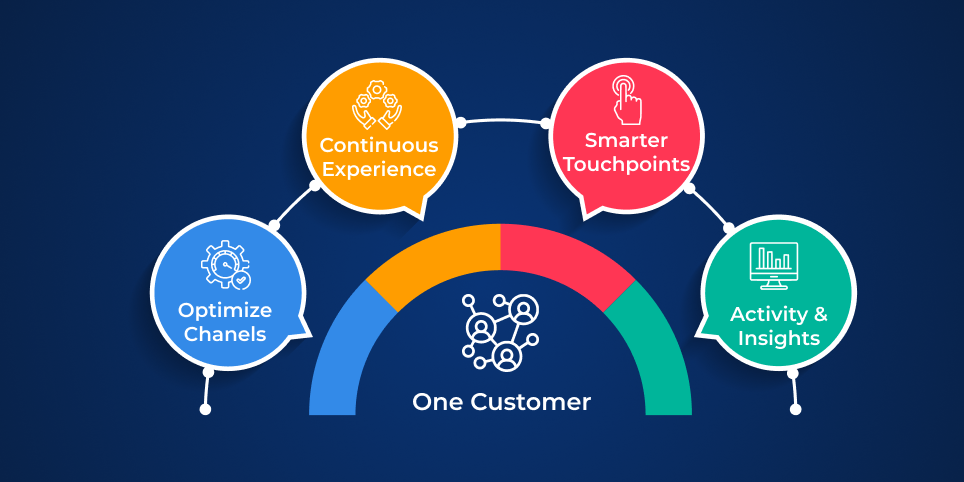
Benefits of CDP
CDP is a transformational technology. The data-driven real-time marketing is transformational and makes the brand more trusted via better governance, getting the maximum out of the current tech stack, and less pain for data professionals spending a long hour processing and batching data.
Deliver single view of customers: CDP unity is the third and first source for forming a 360-degree comprehensive view of the customers over channels and devices, making the data available to the other tech as well as across the business.
Customer and Marketing Experience: Customers use more devices and channels than before while demanding relevant and exceptional experiences. With the comprehensive set of customer data. CDPs fuel cross and multi-channel marketing with trusted and comprehensive data.
Data Silos and Tear Down: The value of customer data extends over a business. The CDPs provide teams with the capability of leveraging and accessing customer data over departments effectively and accurately.
Putting customers at the center: For enacting customer-centered marketing, companies must be aware of their customers. The CDPs equip the business in managing customer relationships as well as marketing with the audience in mind.
CRM vs. DMP vs. CDP
There exists some confusion regarding the benefits and differences between the CRM (Customer Relationship Management) platform, DMP (Data Management Platform), and CDP (Customer Data Platform). While all of these manage customer data similarly, they are all built for different purposes and possess some significant variations.
A CDP is a centralized database that builds unified profiles from the data it collects over any quantity of disparate data silos. Then, CDP delivers combined data to other solutions in the technology stack to affect the customer experience.
A DMP is software that is used by marketers for improving media buying, retargeting, and advertising for programmatic advertising. The DMP will be feeding its data into the CDP for improving the customer profiles that a CDP develops.
A CRM platform is used to manage and track interactions with prospects and customers. Primarily they support the sales team for sales management and content management.
In application, CDP is a much broader term, and it positions itself on the top of the CRM and DMP solutions in the technology stack. The customer data platform can ingest third and second-party data from CRMs and DMPs to make the unified profiles they create more complete. Whereas, a DMP can also benefit from a CDP because it can ingest data for improving targeting.
Top CDP Software Benefactors
There are several CDPs made for the business of every size and shape. Here are some popular markets to help to begin your search
Segment: It is the CDP helping businesses unify and collect customer data over several online sources and channels. The idea is to offer businesses an integrated and complete view of the customer journeys over every touchpoint. Users can connect customer data over data warehousing tools, analytics, and 300 marketing.
Emarsys: It helps businesses to build an omnichannel approach by analyzing and collecting data from various sources. The features include analytics and reporting, personalization, cross-channel automation, and industry-specific solutions, which includes retail, travel, and e-commerce.
Exponea: It is a customer data end-to-end platform focused on B2C and e-commerce businesses. This solution helps the companies in connecting as well as tracking offline and online data across sources and channels for providing a single customer view as well as creating personalized campaigns.
Optimove: With CDP at its core, this is a hub of relationship marketing. It first collects, then segments, and finally analyzes customer data to help the business to transform it into actionable insight. The technology of the company suite enables the optimization, tracking, and creation of multi-channel, personalized campaigns.
Tealium AuduienceStream CDP: It helps businesses in enhancing audience engagement as well as build comprehensive customer profiles. These data within the profiles can help the companies define low or high-value customers and identify the milestones that may be used for segmenting audiences and driving key engagement insights.
Wrapping up
Without customers, it is quite impossible to have a business. Customers belong to the center of everything that businesses do, particularly marketing. To place those in the center and front, raw and real customer data are required. Customer Data Platform provides unity, accuracy, and intimacy that is required for aligning the organizations, engaging the customers, and inspiring the marketing. CDPs are complex pieces of software. Using one correctly can provide you with a deeper understanding of the customers. You will be able to take the knowledge as well as improve your sales, marketing, and even the products. CDP is going to the perfect, too, if businesses wish to take the upcoming steps towards understanding the customers.



